Description
Doctorfish is a type of surgeonfish, a group that is named for the sharp, blade-like spine on both sides of the caudal peduncle (the base of the tail).
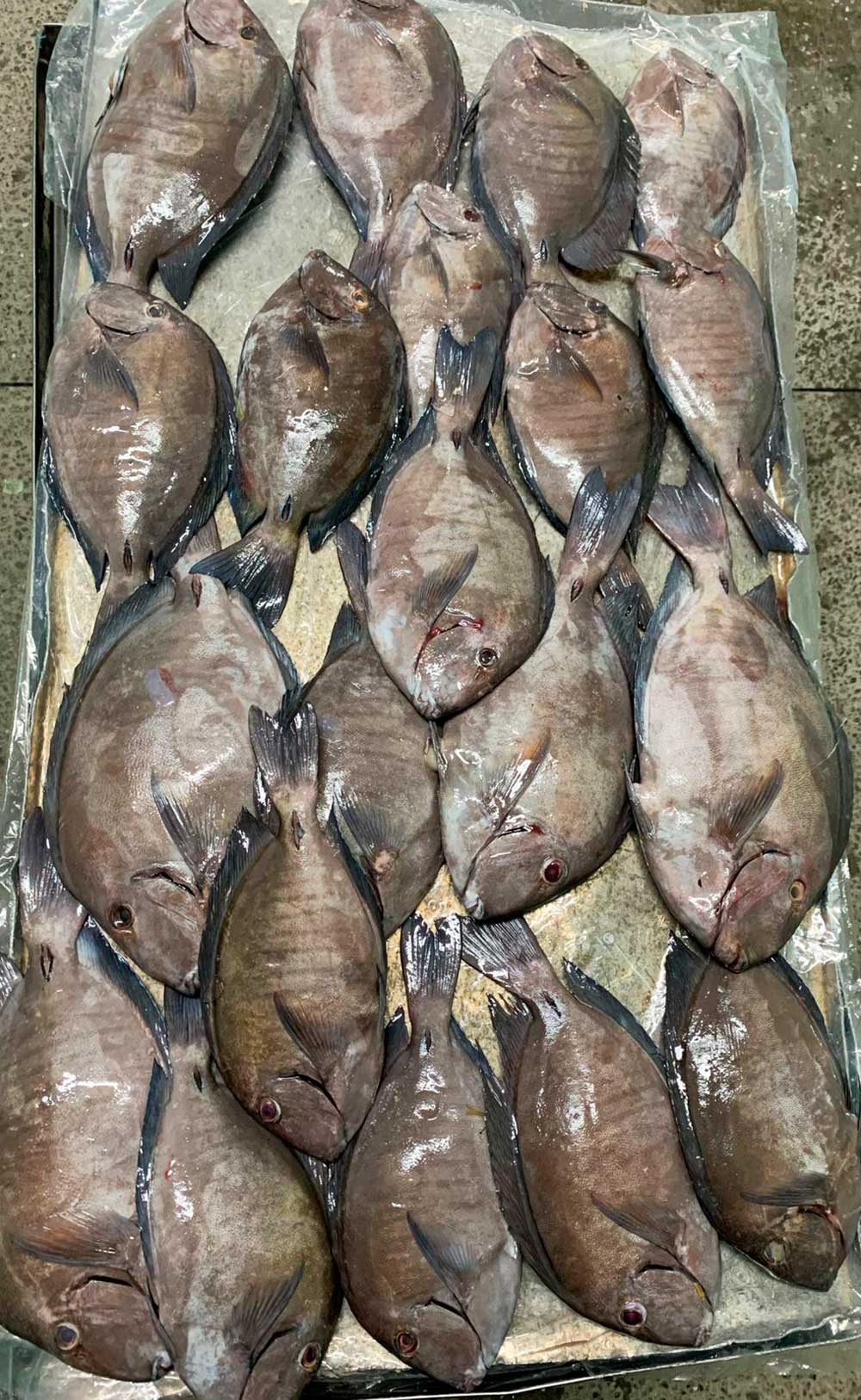
The Doctorfish, Acanthurus chirurgus, gets its common name for the structures called “scalpels”, which are found on either side of the caudal peduncle.
The “scalpel” is used during fights with other doctorfish and as a defense mechanism against predators. Its coloration generally varies from blue-gray to dark brown. From 10 to 12 vertical bars are always present, but often faint. The edges of the caudal, dorsal, and anal fins are blue. There is also a faint blue ring that can be seen encircling the “scalpel” on either side.
The Doctorfish is found at maximum size of 15 inches and 11 pounds, although it is most commonly about 10 inches (25 cm) in length.
Where can Doctorfish be found?
They are widely spread throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of Western Atlantic. They are located from the North of the Gulf of Mexico, to Sao Paulo in Brazil; 37°N-7°S, 89°W-34°W (Fig. 2). They are commonly found in the shallow, rocky reefs of the West Indies. They are native to Trinidad and Tobago along with many other islands such as Jamaica, Grenada and Barbados. Its distribution also includes the Atlantic from Massachusetts to Brazil. In the Eastern Atlantic, it is reported from Ascension and St. Helena Islands and Senegal, West Africa.
Doctorfish occupy various habitats. Some may occupy reefs while others may occupy the sandy bottoms of the oceanic bed. They tend to occupy shallow areas of reefs as well as rocky habitats (Fig. 3). Juveniles occupy seagrass beds as well as mangroves. Water depths range from 2-25m. They are documented as diurnal due to their eating habits. Doctorfish tangs are typically herbivores, their diet mainly consists of benthic (bottom-living) algae.
The Doctorfish is typically found among rocky outcrops and coral reefs. This species prefers shallow reefs and rocky areas. It occurs in loose aggregations.
How do Doctorfish behave?
Doctorfish tend to swim singly, in pairs or in small aggregations. These aggregations are made up of either their species or related species. They are not too much of an aggressive organism yet they possess territorial traits to an extent. According to IUCN Red List, Doctorfish tang can live up to a maximum of 43 years. It has been recorded in Lee Stocking Island, Bahamas, that these species can live up to 27 years and in San Blas, Panama, up to 16 years. Doctorfish tang survival years fluctuate from 8 to 37 years. Their survival rate is affected due to the stress level of the environment they occupy. These ratings are bases on noncaptivity observations. Their lifespan in captivity is usually up to 7 years. They tend to be abundant along the Caribbean strip as they favour the water’s warmth and rocky environs.
Doctorfish spends its daylight hours grazing on algae and organic detritus. Its teeth are specially shaped for scraping algae and plant matter from rocks. Because it swallows its food whole, it has a gizzard-like organ in the intestine filled with particles of sand which help to grind food before it starts the digestive process.
Spawning occurs in the open ocean, typically around the evening time of the lunar cycle leaving behind fertilized eggs. At this time, the sea current is strongest and the tidal ranges are the largest. These groups consists of one male to one or more females (Robertson, 2008). Fertilization is external as the females lay their eggs and the males fertilize them. Multiple eggs are laid, each consisting of an oil droplet enabling them to float, thus making them pelagic. Egg’s diameter are no larger than 1mm. These eggs are hatched within 24 hours into larvae which grow into the acronurus stage (a special stage found in tangs and surgeonfish – Fig. 4). They are commonly found close to the shore. No parental care is given to the young ones – they are left to survive on their own. Fertilization occurs during evening hours in a group event, where each egg is less than a millimeter in diameter and contains a small amount of oil for flotation. The translucent, plankton-like larvae hatch within 24 hours of fertilization. They are laterally compressed and diamond-shaped with large eyes and pectoral fins. Many body parts, such as scales and the dorsal and anal fins, do not develop until the larvae have reached 2–6 mm in length. The “scalpel” does not appear until they are about 13 mm long. As the “scalpel” grows, the anal and dorsal spines shrink. Once the fish reaches around 25 mm in length, it moves to the bottom where it continues to grow, eventually reaching sexual maturity in roughly nine months.
This species possess anti-predator adaptations such as their razor-sharp caudal spine, congregation attacks and sometimes, their colourful appearance. Their aposematic (warning) colourful appearance sends a message of their characteristics of poisonous skin and venomous spine to their predators. These fish communicate by changing their body colouration due the condition and their perception on the environment. For example, high stress level environs will result in their skin to deepen in their blue colouration. This effect is due to iridiophores (reflecting bodies) which causes the brighter blue colouration to become smaller and less iridescent, thus producing a darker shade of blue. Change in skin colouration can send messages such as male dominance or warning signals depending on the highlighted area on the fish’s body; such as the colouration along the caudal spine.
How does Doctorfish looks like?
Their body colour ranges from blue-grey, grey to dark brown. Their colour depends on the occupied habitat. 10-12 narrow vertical bars are present on their sides, which help separate them from other regional Acanthurus species. Their fins are blue with a lighter band of blue on their tail fin. A dark spine-like structure is located on each side of the caudal peduncle (base of the tail fin), with the groove edged in blue (Fig. 1). These spines fold into their grooves when they are not in use. Their teeth are designed for scraping algae off of corals and rocks. Internally, they possess a gizzard like organ as their way of digesting the sand and other food sources they ingest whole. Doctorfish tang’s length have been recorded to reach up to 39cm; weighing up to 11kg. However, its common growth size is 25cm long with 5kg in weight.
Doctorfish is grey to brown in color with approximately ten faint, well-spaced vertical dark bars on its sides. Displays a bright blue edge around its spine.
What do doctorfish eat?
Doctorfish consumes benthic algae and zooplankton, where it serves as important role on the reef in preventing fast-growing algae from over-growing hard coral.
A gizzard-like organ in the intestines contains sand particles, which aid in grinding up food prior to digestion.
What are the health benefits of eating Doctorfish?
Doctorfish are a nutritious choice for you and your family. Here are 5 reasons why you should eat doctorfish, or any other fish in general.
Fatty fish like Doctorfish contain nutrinents such as the famous fat-soluble vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids. To meet your omega-3 requirements, it is recommended to eat fat from fish at least once or twice a week.
Doctorfish may lower your risk of heart attacks and strokes. That´s why fish in general is considered by many as the best food to eat to maintain a healthy heart due to the presence of these omega-3 fatty acids.
Doctorfish may increase grey matter in the brain and protect it from age-related deterioration: Studies have shown that people who eat fish every week have more grey matter in the centers of the brain that regulate emotion and memory.
Doctorfish may help prevent and treat depression, making you a happier person. Omega-3 fatty acids can be beneficial against depression, both on their own and when taken with antidepressant medications.
Lastly, fish consumption is linked to reduced risk of autoimmune diseases. Several studies have found that omega-3 or fish oil consumption is linked to reduced risk of type 1 diabetes in children, as well as a form of autoimmune diabetes in adults. The results are preliminary, but researchers believe that this may be caused by the omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D in fish and fish oils.
Culinary profile:
Doctorfish is a delicious fish, really popular in jamaica where its appreciated mostly steamed or stewed. This typical Caribbean/Jamaican fish is one of the most popular in that region, resulting in in many admirers amongst top chefs world-wide. All Caribbean Jamaican seafoods are cooked with country seasonings, check bellow for a few suggested recipes.
Doctorfish videos
Doctorfish articless
Doctorfish nutrition facts
- Serving size: 3 ounces
- Calories: 83 kcal
- Protein: 19.9 grams
- Carbohydrate: 0 g
- Total fat: 0.4 grams
- Calcium: 43.2 mg
- Iron: 1.33 mg
- Omega3: 0.165 grams
- Selenium: 10.7 μg
- VitaminA: 11.1μg
- Zinc: 1.8 mg




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.